HtmlTemplatePlugin
이번엔 써드 파티 패키지(웹팩 기본 플러그인이 아니라는 뜻)에 대해 알아보자.
HtmlTemplatePlugin은 HTML 파일을 후처리하는데 사용한다.
빌드 타임의 값을 넣거나 코드를 압축할 수 있다.
지금같은 경우에는
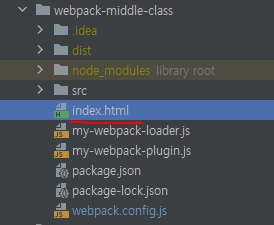
index.html 파일을 src폴더 바깥에 만들어놓은 상태다.
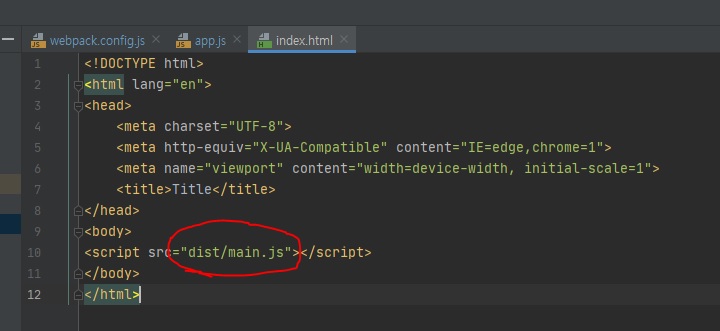
그래서 빌드한 결과물과 연동시키기 위해서 위와 같이 직접 입력했었는데, 웹팩에서 html 파일도 빌드 과정에 넣고 싶다면, 이 플러그인을 사용하면 된다.
npm i -D html-webpack-plugin
그리고 위의 index.html 파일을 src 폴더 안으로 옮겨 앞으로 웹팩으로 관리해보도록 하자.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
그리고 기존에 있던 빌드 결과물과 연동한 <script> 부분은 지우자.
그리고 webpack.config.js 파일에서 방금 설치한 html-webpack-plugin을 세팅해보자.
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const childProcess = require('child_process');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
entry: {
main: "./src/app.js"
},
output: {
path: path.resolve('./dist'),
filename: "[name].js"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader'
],
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
publicPath: './dist',
name: '[name].[ext]?[hash]',
limit: 20000, // 20kb
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.BannerPlugin({
banner: `
Build Date: ${new Date().toLocaleString()}
Commit Version: ${childProcess.execSync('git rev-parse --short HEAD')}
Author: ${childProcess.execSync('git config user.name')}
`
}),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
TWO: JSON.stringify('1+1'),
'api.domain': JSON.stringify('http://dev.api.domain.com')
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html'
})
]
}
옵션을 전달할 때 template 키로 템플릿 경로를 전달할 수 있다.
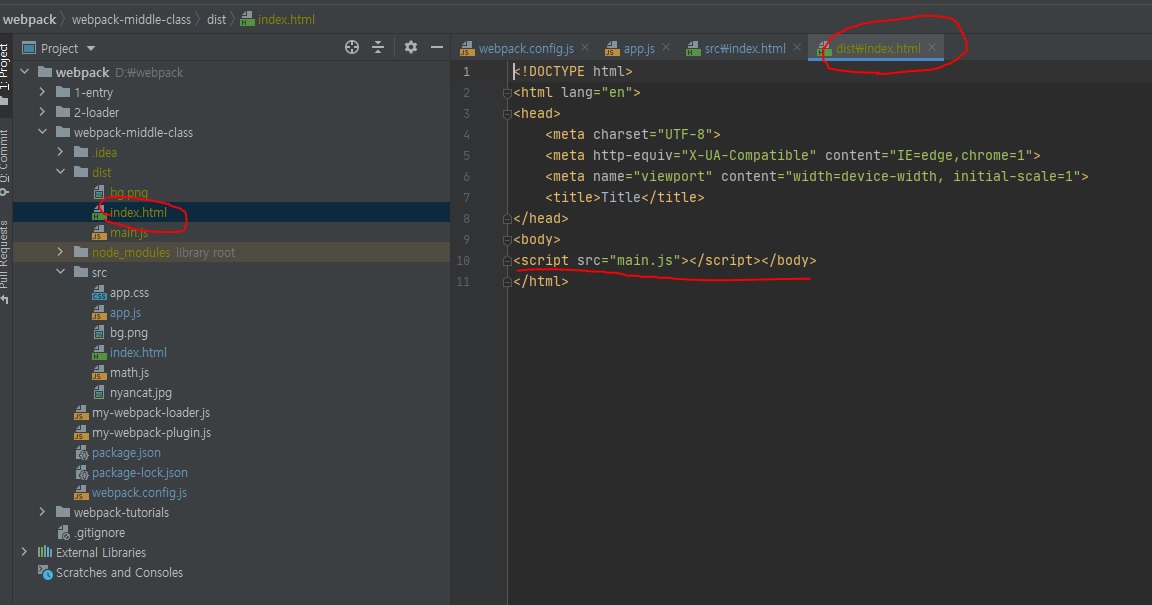
아까와는 다르게 dist 폴더에 index.html 파일이 들어온 것을 볼 수 있다.
이렇게 html-webpack-plugin을 사용하면 빌드과정에 html도 포함하기 때문에 좀 더 의존적이지 않은 코드로 html을 만들 수 있다.
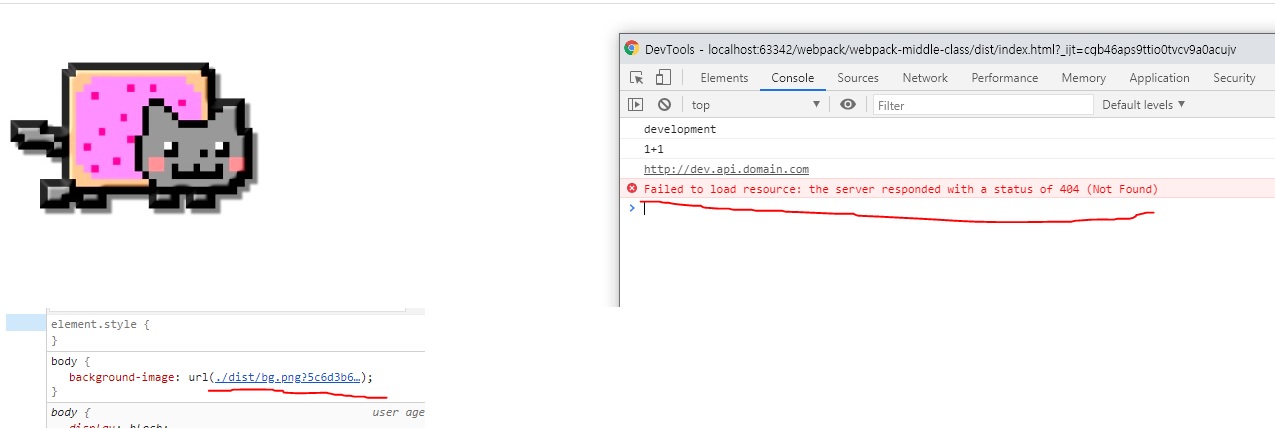
dist/index.html을 실행해보면 위와 같이 오류가 난 것을 확인할 수 있다.
경로가 잘못된 것을 볼 수 있다.
이거는 이미지를 처리하는 파일 로더 부분을 수정해주면 해결이 된다.
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const childProcess = require('child_process');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
entry: {
main: "./src/app.js"
},
output: {
path: path.resolve('./dist'),
filename: "[name].js"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader'
],
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
// publicPath: './dist',
name: '[name].[ext]?[hash]',
limit: 20000, // 20kb
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.BannerPlugin({
banner: `
Build Date: ${new Date().toLocaleString()}
Commit Version: ${childProcess.execSync('git rev-parse --short HEAD')}
Author: ${childProcess.execSync('git config user.name')}
`
}),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
TWO: JSON.stringify('1+1'),
'api.domain': JSON.stringify('http://dev.api.domain.com')
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html'
})
]
}
html-webpack-plugin을 사용하면 좀 더 유동적으로 html을 만들어낼 수 있다.
예를 들어서
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title(dev)</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
개발 버전일 경우에는 title에 (dev)라고 넣고 그렇지 않을 경우엔 (dev)를 빼고싶다.
이런 기능도 이 플러그인에서 제공한다.
위 title 부분에 아래와 같이 ejs 문법을 넣어보자.
아래는 env라는 변수를 넣을 수 있다.
웹팩 쪽에서 이 env 변수 값을 넣어주면 된다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title<%= env %></title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const childProcess = require('child_process');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
entry: {
main: "./src/app.js"
},
output: {
path: path.resolve('./dist'),
filename: "[name].js"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader'
],
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
// publicPath: './dist',
name: '[name].[ext]?[hash]',
limit: 20000, // 20kb
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.BannerPlugin({
banner: `
Build Date: ${new Date().toLocaleString()}
Commit Version: ${childProcess.execSync('git rev-parse --short HEAD')}
Author: ${childProcess.execSync('git config user.name')}
`
}),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
TWO: JSON.stringify('1+1'),
'api.domain': JSON.stringify('http://dev.api.domain.com')
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',
templateParameters: {
env: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? '(개발용)' : ''
}
})
]
}
templateParameters 라는 키에 env 변수를 만들어 process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? '(개발용)' : '' 값을 전달하면 된다.
NODE_ENV=development npm run build
위와 같은 명령어를 실행해보자.
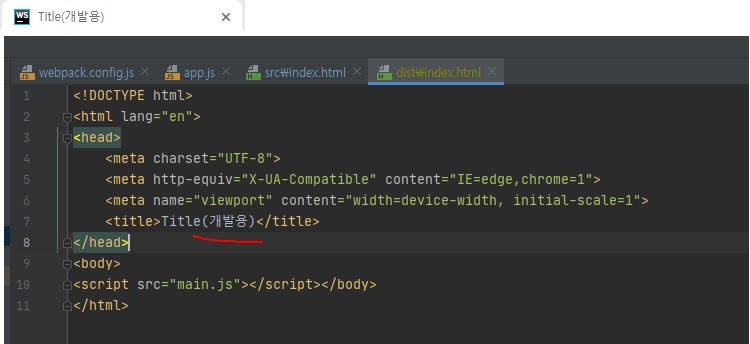
NODE_ENV=production npm run build
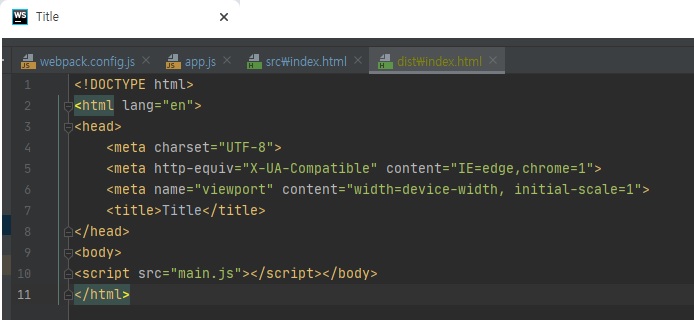
반대로 production이라고 설정하면 위와 같이 (개발용)이라는 문구가 들어가지 않은걸 볼 수 있다.
이런식으로 개발환경에서는 타이틀 옆에 (개발용)이라는 문자가 있으면 개발환경이고 없으면 운영 환경이구나 라는 것을 알릴 수 있다.
이것 뿐만이아니라
- html을 압축하고
- 주석을 제거하는
기능도 있다.
테스트로 index.html에 주석을 달아보도록 하겠다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Title<%= env %></title>
<!-- 이것은 주석입니다. -->
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const childProcess = require('child_process');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
entry: {
main: "./src/app.js"
},
output: {
path: path.resolve('./dist'),
filename: "[name].js"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader'
],
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
// publicPath: './dist',
name: '[name].[ext]?[hash]',
limit: 20000, // 20kb
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.BannerPlugin({
banner: `
Build Date: ${new Date().toLocaleString()}
Commit Version: ${childProcess.execSync('git rev-parse --short HEAD')}
Author: ${childProcess.execSync('git config user.name')}
`
}),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
TWO: JSON.stringify('1+1'),
'api.domain': JSON.stringify('http://dev.api.domain.com')
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',
templateParameters: {
env: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? '(개발용)' : ''
},
minify: {
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeComments: true,
}
})
]
}
collapseWhitespace는 공백을 없애주는 거고 removeComments는 주석을 없애주는 옵션이다.
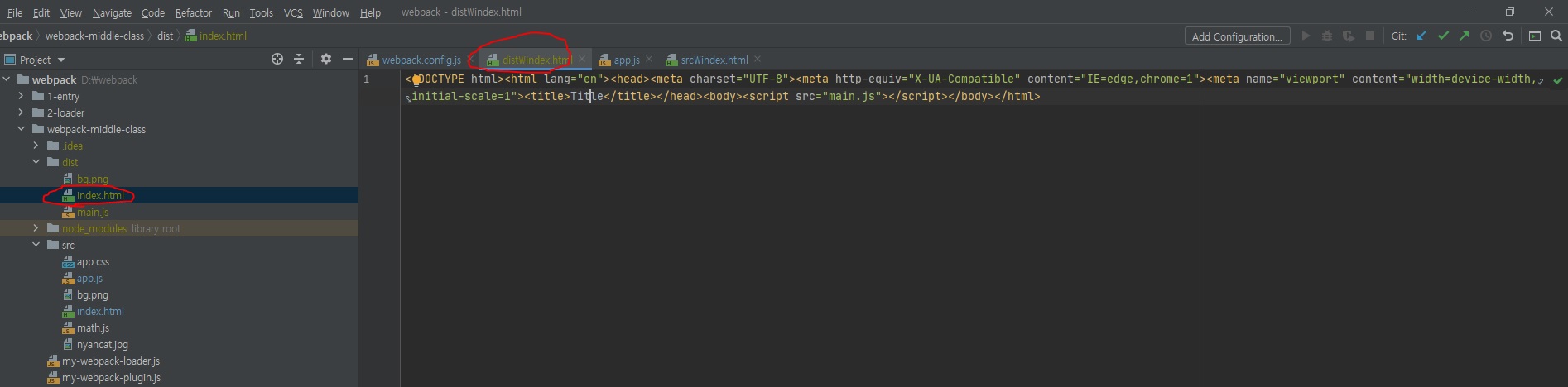
빌드하고 빌드된 dist/index.html 파일을 보면 빈칸이 다 없어졌기 때문에 한줄로 코드가 다 바뀌었고, 바디쪽에 입력했던 주석도 제거된 것을 볼 수 있다.
이것 또한 production 일 경우만 적용하는 것이 편하다.
development 환경에선 사용 안하는 것이 좋다.
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const childProcess = require('child_process');
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
entry: {
main: "./src/app.js"
},
output: {
path: path.resolve('./dist'),
filename: "[name].js"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader'
],
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
// publicPath: './dist',
name: '[name].[ext]?[hash]',
limit: 20000, // 20kb
}
}
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.BannerPlugin({
banner: `
Build Date: ${new Date().toLocaleString()}
Commit Version: ${childProcess.execSync('git rev-parse --short HEAD')}
Author: ${childProcess.execSync('git config user.name')}
`
}),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
TWO: JSON.stringify('1+1'),
'api.domain': JSON.stringify('http://dev.api.domain.com')
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html',
templateParameters: {
env: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? '(개발용)' : ''
},
minify: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? {
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeComments: true,
} : false
})
]
}