- javascript는 몇가지 type이 있는가?
-
javascript에는 크게 두 가지 타입이 있다.
이건 자바스크립트라는 언어에 국한된게 아니고 대부분의 언어의 공통 사항이다.
- 1. 값이 담겨있는 primitive type
- 2. 주소값이 담겨있는 reference type
primitive 타입에는 String, Number,Boolean, null, undefined, 그리고 es6에 추가된 symbol 까지 6가지가 있고, reference type에는 object가 있다.
reference(주소값)을 직접 다루는 언어는 c, c++이 있다.
다른 언어들은 주소값을 직접 다루는 연산자는 없지만
이 개념을 분명히 알고 있어야 call by value와 call by reference의 차이점을 이해할 수 있고,
shallow copy와 deep copy의 차이점을 이해할 수 있고
리액트에서 자주 나오는 immutable의 의미를 이해할 수 있다.
- Reference type이란?
-
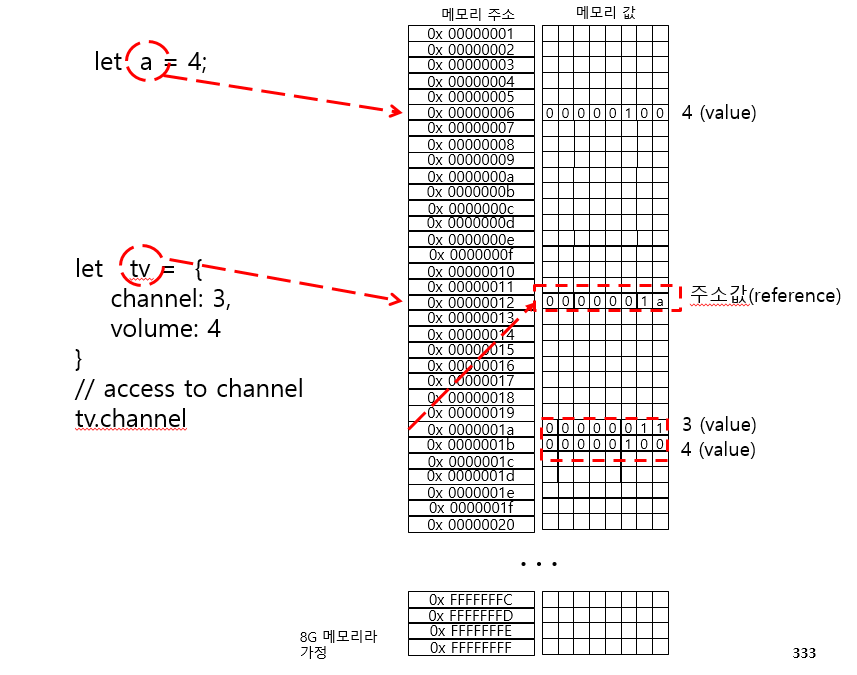 a라는 변수는 6번지 주소를 가르키고 있고 6번지에 실제 값인 4가 저장되어있다.
a라는 변수는 6번지 주소를 가르키고 있고 6번지에 실제 값인 4가 저장되어있다.
그러나 tv 객체 변수에는 channel 과 volume라는 값을 1a 번지와 1b 번지에 연속된 메모리 공간에 저장 후
시작 번지인 1a번지를 12번지에 저장하고 tv가 가르키는 12번지는 실제 값이 들어가 있는 것이 아니라 값이 저장된 메모리 주소를 가르키고 있다.
tv 변수는 실제 값이 아니라 값이 저장된 메모리 주소를 참조해서 찾아가기 때문에 reference 라고 부르고,
channel 값에 접근하기 위해서는 tv라는 12번지를 참조(reference)해서 첫번째 인덱스를 찾게 된다.
그래서 . 이라는 연산자는 래퍼런스(reference) 연산자라고 부른다.
tv 메모리 주소를 reference 해서 찾는다는 의미이다.
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4},
];
- unshift
-
Q: title “Cinderella”, price 30$, author “Perrault, rank 5 의 객체를 배열 맨 앞에 추가하시오.
자바스크립트 배열의 맨 앞에 추가하기 위해 Array.Prototype.unshift 함수를 사용한다.
리터럴 객체로 book을 생성한 다음 unshif에 넣고 콘솔 로그로 확인한다.
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4},
];
let book = {title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5};
books.unshift(book); // 5 (해당 배열의 length 값이 반환됨)
console.log(books);
// 결과값 : 원래 books가 변경됨
books = [
{title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5},
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
- shift
-
배열 맨 앞에 객체를 삭제하는 함수이다.
let books = [
{title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5},
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
books.shift(); // {title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5} 삭제되는 맨앞 객체가 반환됨
// 결과값 : 원래 books가 변경됨
books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
- push
-
배열 맨 끝에 객체를 추가하는 함수이다.
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
let book = {title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5};
books.push(book); // 5 (해당 배열의 length 값이 반환됨)
// 결과값 : 원래 books가 변경됨
books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4},
{title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5}
];
- pop
-
맨 끝에 객체를 삭제하는 함수이다.
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4},
{title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5}
];
books.pop(); // {title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5} 삭제되는 맨끝 객체가 반환됨
// 결과값 : 원래 books가 변경됨
books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
];
- splice
-
배열의 맨 앞에 추가, 삭제는 unshift, shift였고 맨 뒤쪽에 추가 삭제는 push, pop이었다.
이번에는 중간에 추가 삭제를 해본다.
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
];
let book = {title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5};
books.splice(1, 0, book); // [] 빈 배열 반환 (잘라낸 객체 반환)
// 2번째부터 0개까지 객체 잘라내고 그 자리에 book을 끼워넣어!
// 결과값 : 마찬가지로 원래 books가 변했음
books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
books.splice(1, 1); // {title: "Cinderella", price: 30, author: "Perrault", rank: 5} 삭제된 객체 반환
// 결과값 : 마찬가지로 원래 books가 변형
books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
- find
-
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
// const b = books.find((item) => item.title === "Swallow's gift");
const b = books.find(function(item){
if(item.title === "Swallow's gift"){
return true; // true값 리턴이지만 b에 true값이 들어가는 것이 아닌 해당 객체가 들어감
}
})
b.author = "Tom";
// 결과값
books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Tom", rank: 4}
]
find를 MDN 사이트에서 찾아보면 아래와 같은 설명이 나온다.
The find() method returns the value of the first element in the provided array that satisfies the provided testing function.
find는 배열을 루프를 돌면서 testing function을 수행한다.
이것을 predicate라고 한다. (test = predicate)
조건을 만족시키면 true를 리턴하고 그렇지 않으면 false를 리턴한다.
그리고 true를 리턴하면 그 즉시 루프를 멈추고 현재 객체를 리턴하게 된다.
만일 찾지 못한다면 undefined를 리턴한다.
위의 문장을 arrow 펑션으로 변경하면 다음과 같다.
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
const b = books.find((item) => item.title === "Swallow's gift");
// const b = books.find(function(item){
// if(item.title === "Swallow's gift"){
// return true; // true값 리턴이지만 b에 true값이 들어가는 것이 아닌 해당 객체가 들어감
// }
// })
b.author = "Tom";
// 결과값
books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Tom", rank: 4}
]
Q. const 라는 키워드는 es6에 새로 등장한 것으로 변수의 스코프가 있으나 값을 한번 할당하면 더 이상 할당할 수 없는 final 개념의 변수 선언 방식이다.
그런데 처음에 const b에 값을 할당 했는데 그 다음에 b.author = 'Tom'을 또 할당하는 것이 가능한가?
b라는 변수는 reference 타입으로 메모리 주소값을 저장하고 있다.
b.author은 해당 메모리의 주소를 참조해서 author의 값을 바꾸라는 의미이므로 b의 메모리 주소값이 바뀐 것이 아니므로 가능하다.
- forEach
-
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
let sum = 0;
books.forEach(item => sum += item.price);
// books.forEach(function(item){
// sum += item.price
// })
// 결과값 95
forEach는 단순히 루프만 반복하는 메서드이다.
물론 reduce 같은 조금 복잡한 함수도 있지만 위와 같이 하는 것이 가장 클린한 코드이다.
- filter
-
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
books.filter(item => item.rank < 3);
// {title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1}
// {title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2}
// 해당 배열의 rank 프로퍼티의 값이 3보다 작은 객체들이 반환된다.
// 이 상태에서 books를 찍어보면, 위 배열이 반환된다.
// 원본 books 배열이 변형되지 않는다.
const highRankList = books.filter(item => item.rank < 3);
// 결과값
highRankList = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2}
]
MDN 사이트에서 filter의 정의를 찾아보면 다음과 같다.
The filter() method creates a new array width all elements that pass the test implemented by the provided function.
여기서 가장 중요한 키워드는 새로운 배열을 리턴한다는 것이다.
즉, 원본 배열을 손상시키지 않는다.
이러한 Array 함수를 immutable 함수라고 부르고 리액트에서 가장 많이 사용되는 용어 중에 하나이다.
- map
-
// 아래 실행결과를 예측하고 map과 forEach의 차이점을 설명하시오.
var items = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5'];
var newItems = items.map(item => parseInt(item));
console.log(items); // ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5']
console.log(newItems); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
var newItems2 = items.forEach(item => parseInt(item));
console.log(items); // ["1", "2", "3", "4", "5"]
console.log(newItems2); // undefined
// map은 루프를 돌려서 리턴되는 값을 순서대로 매치시켜 다시 배열로 만듦
// map은 원본 배열을 손상 X - immutable 메소드
// forEach는 그냥 루프만 돌고 끝 리턴되는게 없다
let books = [
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1},
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4}
]
const rankTitle = [...books]
.sort((a, b) => {
// 오름차순 내림차순 정렬, abc...순서대로
if (a.title > b.title) {
return 1;
} else if (a.title < b.title) {
return -1
} else {
return 0;
}
})
.map((item, index) => `${index + 1}. ${item.title}`)
// 위의 식에서 sort 메서드까지 진행된 후의 결과값
[
{title: "Alice in Wonderland", price: 25, author: "Carroll", rank: 2},
{title: "Seven Dwarfs", price: 35, author: "Disney", rank: 3},
{title: "Swallow's gift", price: 15, author: "Unknown", rank: 4},
{title: "Three Little Pigs", price: 20, author: "Jacobs", rank: 1}
]
// 위의 식에서 map 메서드까지 진행된 후의 결과값
["1. Alice in Wonderland", "2. Seven Dwarfs", "3. Swallow's gift", "4. Three Little Pigs"]
제목으로 소팅하기 위해서 sort 함수를 먼저 사용하게 되면 원본 배열이 손상된다.
sort 함수는 immutable 함수가 아니므로 먼저 원본 배열을 deep copy 해야 한다.
deep copy 하는 방법은 Object.assign() 또는 ... 이라는 스프레드 연산자를 사용해서 한다.
deep copy를 한 후에는 제목으로 소팅한다.
소팅 후 결과는 array 이므로 다시 map이라는 함수를 체인으로 연결해서 사용한다.
MDN에 정의한 map의 정의를 살펴보자
The map() method creates a new array with the results of calling a provided function on every element in the calling array.
map도 filter와 마찬가지로 새로운 배열을 리턴한다는 키워드가 가장 중요하고 마찬가지로 원본 배열을 손상하지 않는 immutable 함수이다.
map이 리턴한 것을 모아서 새로운 배열을 만들어 주므로 우리가 원하는것은 제목만 갖고 만든 스트링 배열이므로 인덱스에 1을 더해준다.
` 빽 틱을 양쪽에 사용한 것은 es6에 새롭게 등장한 탬플릿 스트링이라는 문법이다.
빽틱 안쪽에서 자바스크립트 변수를 사용하기 위해서는 &{변수} 형태로 사용한다.
 a라는 변수는 6번지 주소를 가르키고 있고 6번지에 실제 값인 4가 저장되어있다.
a라는 변수는 6번지 주소를 가르키고 있고 6번지에 실제 값인 4가 저장되어있다.