async function / await
async function 선언은 AsyncFunction 객체를 반환하는 하나의 비동기 함수를 정의합니다.
비동기 함수는 이벤트 루프를 통해 비동기적으로 작동하는 함수로, 암시적으로 Promise를 사용하여 결과를 반환합니다.
그러나 비동기 함수를 사용하는 코드의 구문과 구조는, 표준 동기 함수를 사용하는 것과 많이 비슷합니다.
또한 async function expression을 사용해서 async function을 선언할 수 있습니다.
function resolveAfter2Seconds() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('resolved');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function asyncCall() {
console.log('calling');
const result = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(result);
// expected output: 'resolved'
}
asyncCall();
Syntax
async function name([param[, param[, ... param]]]) {
statements
}
매개변수
- name : 함수의 이름
- param : 함수에게 전달되기 위한 인자의 이름
- statements : 함수 본문을 구성하는 내용
반환 값
Promise : async 함수에 의해 반환된 값으로 해결되거나 async 함수 내에서 발생하는 캐치되지 않는 예외로 거부되는 값
Description
async 함수에는 await 식이 포함될 수 있습니다.
이 식은 async 함수의 실행을 일시 중지하고 전달된 Promise의 해결을 기다린 다음 async 함수의 실행을 다시 시작하고 완료 후 값을 반환합니다.
await 키워드는 async 함수에서만 유효하다는 것을 기억하십시오.
async 함수의 본문 외부에서 사용하면 SyntaxError가 발생합니다.
async/await함수의 목적은 사용하는 여러 promise의 동작을 동기스럽게 사용할 수 있게 하고, 어떠한 동작을 여러 promise의 그룹에서 간단하게 동작하게 하는 것이다.
promise가 구조화된 callback과 유사한 것 처럼 async/await또한 제네레이터(generator)와 프로미스(promise)를 묶는것과 유사하다.
Examples
var resolveAfter2Seconds = function() {
console.log("starting slow promise");
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(function() {
resolve(20);
console.log("slow promise is done");
}, 2000);
});
};
var resolveAfter1Second = function() {
console.log("starting fast promise");
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(function() {
resolve(10);
console.log("fast promise is done");
}, 1000);
});
};
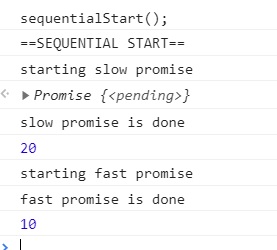
var sequentialStart = async function() {
console.log('==SEQUENTIAL START==');
// If the value of the expression following the await operator is not a Promise, it's converted to a resolved Promise.
const slow = await resolveAfter2Seconds();
console.log(slow);
const fast = await resolveAfter1Second();
console.log(fast);
}
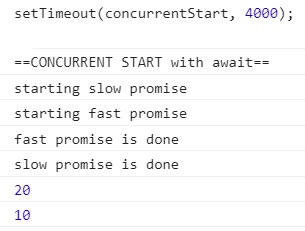
var concurrentStart = async function() {
console.log('==CONCURRENT START with await==');
const slow = resolveAfter2Seconds(); // starts timer immediately
const fast = resolveAfter1Second();
console.log(await slow);
console.log(await fast); // waits for slow to finish, even though fast is already done!
}
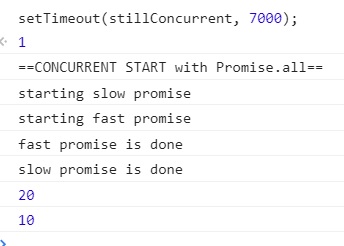
var stillConcurrent = function() {
console.log('==CONCURRENT START with Promise.all==');
Promise.all([resolveAfter2Seconds(), resolveAfter1Second()]).then((messages) => {
console.log(messages[0]); // slow
console.log(messages[1]); // fast
});
}
var parallel = function() {
console.log('==PARALLEL with Promise.then==');
resolveAfter2Seconds().then((message)=>console.log(message));
resolveAfter1Second().then((message)=>console.log(message));
}
sequentialStart(); // after 2 seconds, logs "slow", then after 1 more second, "fast"
// wait above to finish
setTimeout(concurrentStart, 4000); // after 2 seconds, logs "slow" and then "fast"
// wait again
setTimeout(stillConcurrent, 7000); // same as concurrentStart
// wait again
setTimeout(parallel, 10000); // trully parallel: after 1 second, logs "fast", then after 1 more second, "slow"

await 와 Promise#then을 혼동하지 마세요
sequentialStart 에서, 첫 번째 await는 2초의 대기 시간을 갖고, 다시 두 번째 await에서 1초의 대기 시간을 갖습니다.
두 번째 타이머는 첫 번째 타이머가 완료될 때 까지 생성되지 않습니다.concurrentStart 에서, 두 타이머 모두 생성 된 다음 await 합니다.
타이머가 동시에 실행되고 있지만, await 호출은 여전히 연속적 실행중이므로, 두 번째 await 는 첫 번째 호출이 끝날 때 까지 대기합니다.
이렇게하면 3초가 아니라, 가장 느린 타이머에 필요한 2초가 필요합니다.
stillConcurrent 에서도 Promise.all 을 사용하여 같은 일이 발생합니다.두 개 이상의 프러미스를 동시에 wait 하고 싶다면, Promise#then을 사용하여 예제와 같이 parallel 를 수행할 수 있습니다.
async함수를 사용한 promise chain 재작성
Promise 를 반환하는 API는 promise chain을 만들며 여러 파트의 함수로 나뉜다.
아래 코드를 보자.
function getProcessedData(url) {
return downloadData(url) // returns a promise
.catch(e => {
return downloadFallbackData(url) // returns a promise
})
.then(v => {
return processDataInWorker(v); // returns a promise
});
}
위의 코드는 하나의 async함수로 아래와 같이 쓰여질 수도 있다.
async function getProcessedData(url) {
let v;
try {
v = await downloadData(url);
} catch (e) {
v = await downloadFallbackData(url);
}
return processDataInWorker(v);
}
위 예제에서는 return 구문에 await 구문이 없다는 것에 주목하자.
이는 async function의 반환값이 암묵적으로 Promise.resolve로 감싸지기 때문이다.