14.3.5 결정되지 않는 프로미스 방지하기
프로미스는 비동기적 코드를 단순화하고 콜백이 두 번 이상 실행되는 문제를 방지합니다.
하지만 resolve나 reject를 호출하는 걸 잊어서 프로미스가 결정되지 않는 문제까지 자동으로 해결하지는 못합니다.
에러가 일어나지 않으므로 이런 실수는 찾기 매우 어렵습니다.
복잡한 시스템에서 결정되지 않은 프로미스는 그냥 잊혀질 수 있습니다.
결정되지 않은 프로미스를 방지하는 한 가지 방법은 프로미스에 타임아웃을 거는 겁니다.
충분한 시간이 지났는데도 프로미스가 결정되지 않으면 자동으로 실패하게 만들 수 있습니다.
물론 얼마나 기다려야 ‘충분히’ 기다렸는지 스스로 판단해야 합니다.
10분 정도는 걸릴 거로 생각하는 복잡한 알고리즘에 1초 타임아웃을 걸어서는 안 됩니다.
launch 함수에 에러 조건을 넣어 봅시다.
발사하는 로켓은 열 번에 다섯 번은 실패하는 매우 실험적인 로켓입니다.
const EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter;
class Countdown extends EventEmitter {
constructor(seconds, superstitious) {
super();
this.seconds = seconds;
this.superstitious = !!superstitious;
}
go() {
const countdown = this;
const timeoutIds = [];
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
for (let i=countdown.seconds; i>=0; i--) {
timeoutIds.push(setTimeout(function() {
if (countdown.superstitious && i===13) {
// 대기중인 타임아웃을 모두 취소합니다.
timeoutIds.forEach(clearTimeout);
return reject(new Error('Oh my god'));
}
countdown.emit('tick', i);
if (i===0) resolve();
}, (countdown.seconds - i) * 1000))
}
})
}
}
// 이 부분
// 0.5 확률에 의해 return으로 함수가 그냥 종료되던지 또는 실행돼서 resolve값 넘기던지...
function launch() {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
if (Math.random() < 0.5) return; // 문제가..
console.log("Lift off!");
setTimeout(function() {
resolve("In orbit!");
}, 2*1000);
})
}
const c = new Countdown(3, true)
.on('tick', i => console.log(i + '...'));
c.go()
.then(launch)
.then(function(msg) {
console.log(msg);
})
.catch(function(err) {
console.error("Houston, we have a problem...");
})

이 코드는 정말 무책임합니다.
reject를 호출하지 않는데다가, 심지어 콘솔에 기록하지도 않습니다.
열 번 시도하면 그중 다섯 번은 영문도 모른 채 실패하는 셈입니다.
절대 바람직한 일이 아니죠.
다음과 같이 프로미스에 타임아웃을 거는 함수를 만들 수 있습니다.
function addTimeout(fn, timeout) {
if (timeout === undefined) timeout = 1000; // 타임아웃 기본값
return function(...args) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
const tid = setTimeout(reject, timeout, new Error("promise timed out"));
fn(...args)
.then(function(...args) {
clearTimeout(tid);
resolve(...args);
})
.catch(function(...args) {
clearTimeout(tid);
reject(...args);
})
})
}
}
“와~ 프로미스를 반환하는 함수를 호출하는 프로미스를 반환하는 함수를 반환하는 함수?? 뭐가 이리 복잡해!” 하고 외치더라도 충분히 이해할 수 있습니다.
프로미스에 타임아웃을 걸기 위해서는 함수를 반환하는 함수가 필요한데, 절대 쉬운 문제는 아닙니다.
이 함수를 완벽히 이해하는 건 상당한 고급 사용자에게나 가능한 일이니 당장 이해하지 못해도 괜찮습니다.
하지만 이 함수를 사용하는 건 아주 쉽습니다.
프로미스를 반환하는 어떤 함수에든 타임아웃을 걸 수 있습니다.
로켓 과학이 엄청나게 발달해서, 가장 느린 로켓도 10초 안에는 궤도에 들어갈 수 있다고 합시다.
그러면 타임아웃은 11초면 충분합니다.
const EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter;
class Countdown extends EventEmitter {
constructor(seconds, superstitious) {
super();
this.seconds = seconds;
this.superstitious = !!superstitious;
}
go() {
const countdown = this;
const timeoutIds = [];
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
for (let i=countdown.seconds; i>=0; i--) {
timeoutIds.push(setTimeout(function() {
if (countdown.superstitious && i===13) {
// 대기중인 타임아웃을 모두 취소합니다.
timeoutIds.forEach(clearTimeout);
return reject(new Error('Oh my god'));
}
countdown.emit('tick', i);
if (i===0) resolve();
}, (countdown.seconds - i) * 1000))
}
})
}
}
function launch() {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
if (Math.random() < 0.5) return; // 문제가..
console.log("Lift off!");
setTimeout(function() {
resolve("In orbit!");
}, 2*1000);
})
}
// 이 함수로 인해 launch 함수가 0.5 확률로 return 되도
// setTimeout 함수로 일정시간 이후 reject를 전달 할 수 있다.
// 이런식으로 하면 launch 함수의 Promise가 결정이 안되는 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
function addTimeout(fn, timeout) {
if (timeout === undefined) timeout = 1000; // 타임아웃 기본값
return function(...args) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
const tid = setTimeout(reject, timeout, new Error("promise timed out"));
fn(...args)
.then(function(...args) {
clearTimeout(tid);
resolve(...args);
})
.catch(function(...args) {
clearTimeout(tid);
reject(...args);
})
})
}
}
const c = new Countdown(3, true)
.on('tick', i => console.log(i + '...'));
c.go()
.then(addTimeout(launch, 11*1000))
.then(function(msg) {
console.log(msg);
})
.catch(function(err) {
console.error("Houston, we have a problem: " + err.message);
})
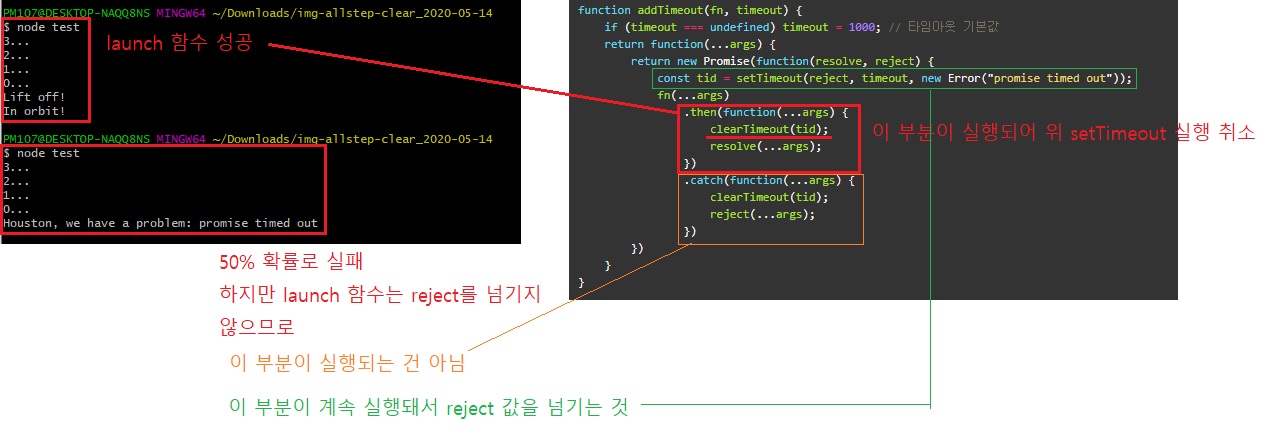
이제 launch 함수에 문제가 있더라도 프로미스 체인은 항상 결정됩니다.