애플 사이트 따라하기 꿀팁내용들
1. 구글폰트 적용
- 구글폰트 사이트
- noto sans 검색
- noto sans KR 선택
- bold 400, 900 선택
- embed link 복사
- link 연동
- 구글폰트 Embed 부분에 있는 CSS rules to specify families 부분 복붙
2. flex, grid 참고자료
3. margin-right: auto;
- margin-right : auto 의 뜻, 오른쪽 여백을 모두 차지하라는 뜻
- CSS 우선순위 상기
4. em, rem 사용론
em은 layout 골격을 담당하는 속성들에게 : 해당 요소의 font-size에 영향을 받게하기 위함rem은 font-size에게 : root element(html)에 영향을 받게하기 위함
5. 각 구간의 인터렉션을 잘 봐야된다.
어떤 구간은 브라우저 width 값만큼 꽉 차있는 경우도 있고, 어떤 구간은 max-width: 1000px 정도로만 차있는 경우도 있다.
그런데 모든 구간을 감싸고있는 container에 max-width: 1000px 을 준다면 그렇지 않은 구간에선 좀 복잡해질 것 이다.
6. 애플 사이트 폰트사이즈 어떤건 vw, 어떤건 rem
이는 디자이너의 의도에 맞추겠다는 의미이다.
애플사이트 타이틀쪽 텍스트는 대부분 vw이고, 설명글들은 대부분 rem이다.
이는 아마 디자인 쪽에서 정해줬을 것이다. 디자인 방향에 의해 조절해야될 문제
7. 인터렉션 구현 컨셉
Timeline : 시간의 흐름을 선으로 표시한 것. 애니메이션은 보통 시간의 흐름에 의해 진행된다.
하지만 지금 우리가 해야되는 애니메이션은 시간의 흐름이 아닌 스크롤의 진행도에 따른 것.스크롤 구간 : 즉 ‘애니메이션 단위’를 나눠야된다. 이는 마크업 때부터 고려되어야 한다.
해당 예제는 스크롤 구간을 마크업에서 4구간으로 나누었듯이 애니메이션도 4구간으로 생각하고 코드를 작성할 것이다.최적화 : 스크롤이 발생할 때마다 전체 애니메이션 구간의 값들이 계산된다면 아주 비효율적이다. 브라우저에 과부하를 끼친다.
애니메이션은 눈에 보여야 의미가 있다.
보이는 장면만 재생이 되면 된다. 두번째 구간에 있는데 첫번째 구간 애니메이션이 계산될 필요가 없다.이를 스크립트 처리할 것이다.
0 ~ 3000px / 3000px ~ 7000px / 7000px ~ 9000px / 9000px ~
이런 식으로 각 구간을 설정해 애니메이션을 발생시킬 것이다.애니메이션 실행 정보
각 스크롤 구간값
0 ~ 3000px : 이 값들을 수정함으로써 애니메이션의 진행속도를 조절할 수 있다.
0 ~ 3000px 을 0 ~ 1000px 로 수정한다면 애니메이션은 3배 더 빠르게 진행될 것이다.
그리고 이 정보를 가지고 스크롤 위치가 0 ~ 3000px 사이라면 3000px 이상 구간의 애니메이션은 실행되지 않도록 할 수 있다.video / img 재생 시간 / 재생 frame 수
- 위와 같은 정보들을 한 배열에 담아놓을 것이다.
그리고 이를 이용해 초기화(default)를 하고 스크롤할 때 해당 애니메이션이 진행되도록 할 것이다.
8. 위치가 고정된 요소의 처리
- fixed / sticky
해당 예제에선 position: fixed를 사용한다.
position 속성에서 sticky와 fixed의 차이점은 다음과 같다.
fixed는 처음부터 고정되어있다.
div {
position: sticky;
top: 2rem;
}
하지만 위와 같이 정의된 sticky div는 top: 2rem 위치가 아닌 곳에선 static처럼 움직이다가 top: 2rem 도착한 곳부터는 fixed로 움직인다.
sticky 속성을 사용못하면 JavaScript로 구현해야된다.
특정 위치에 도달하면 fixed로 아니면 static으로..
여튼 해당 예제에선 fixed를 사용하겠다.
sticky는 IE11 조차도 지원을 안한다.
마이크로소프트에서도 IE11을 버렸다.
하지만, 여전히 사용자들은 IE11을 사용하는 사람이 많기에 fixed를 사용하였다.
애플은 sticky를 사용
IE를 완전히 버린 것은 아니지만 이런 고급진 애니메이션 효과는 IE에선 아예 처리를 안한다.
IE에선 정적인 화면으로 페이지가 노출된다.
- 구간별 sticky 요소 처리
각 구간에 있는 (scroll 할 때 sticky 되어 있어야 되는) 요소를 fixed 처리했다.
그러면 각 구간에 있는 요소들이 전부 겹쳐서 보인다.
자바스크립트로 현재 스크롤 위치가 속한 구간이 어딘지 파악해 안나오도록 해야된다.
이를 class 명, CSS, JavaScript로 제어한다.
아래와 같은 클래스명들이 존재한다.
show-scene-0
show-scene-1
show-scene-2
show-scene-3
scroll-section-0
scroll-section-1
scroll-section-2
scroll-section-3
CSS에선 모든 sticky 요소들에 display: none 처리를 한다.
그리고 위 클래스명을 활용한다.
.sticky-elem {
display: none;
}
.show-scene-0 .scroll-section-0 .sticky-elem,
.show-scene-1 .scroll-section-1 .sticky-elem,
.show-scene-2 .scroll-section-2 .sticky-elem,
.show-scene-3 .scroll-section-3 .sticky-elem {
display: block;
}
JavaScript로 위 show-scene-x 클래스명들을 교체해주면서 각 구간에 맞는 요소들을 보이게해주는 것이다.
9. 스크롤 높이 세팅
- 즉시실행 함수 활용 : 전역변수 영향 X
- 각 scene에 대한 정보 : 객체 4개 만들 것. 애니메이션 구간이 4구간이므로.
(() => {
const sceneInfo = [
{
// 0
type: 'sticky',
heightNum : 5, // 브라우저 높이의 5배로 scrollHeight 세팅할 거란 의미
// 스크롤 높이를 고정값으로 적용하지 않는 이유 - 기기마다 높이가 다르기 때문에 고정값이면 어떤 기기에서는 한참을 스크롤, 어떤 기기에서는 빨리끝
scrollHeight: 0, // 애니메이션 구간 미리 설정
// 초기값을 0으로 설정한 이유 : 어떤 기기에서 해당 페이지를 열지 모르기 때문
// 해당 기기의 브라우저의 viewport height 값의 배수로 적용해줄 것이다.
// 그렇다면 여기서 그렇게 되도록 세팅하면 안되는걸까?
// 그렇게 할 수도 있지만 어차피 창 사이즈 변경에도 대응해야해서 따로 함수로 처리한다.
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0'),
}
},
{
// 1
type: 'normal',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-1'),
}
},
{
// 2
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-2'),
}
},
{
// 3
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-3'),
}
}
];
function setLayout() {
// 각 스크롤 섹션의 높이 세팅
for (let i = 0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight = sceneInfo[i].heightNum * window.innerHeight;
sceneInfo[i].objs.container.style.height = `${sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight}px`;
}
}
// resize도 고려
window.addEventListener('resize', setLayout);
setLayout();
})()
10. 스크롤 처리 기본 개념 잡기
- 몇번째 스크롤 섹션을 스크롤중인지 판별 해야됨
(() => {
let yOffset = 0; // window.pageYOffset 대신 쓸 변수
const sceneInfo = [
{
// 0
type: 'sticky',
heightNum : 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0'),
}
},
{
// 1
type: 'normal',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-1'),
}
},
{
// 2
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-2'),
}
},
{
// 3
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-3'),
}
}
];
function setLayout() {
// 각 스크롤 섹션의 높이 세팅
for (let i = 0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight = sceneInfo[i].heightNum * window.innerHeight;
sceneInfo[i].objs.container.style.height = `${sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight}px`;
}
}
function scrollLoop() {
}
// resize도 고려
window.addEventListener('resize', setLayout);
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
// 현재 스크롤 위치 검사
// video 를 스크롤 위치에 따라 애니메이션 적용할 때는 pageYOffset 값에 약간 변형을 줄 것이다.
// 때문에 상황에 맞는 pageYOffset 값 활용을 위해 pageYOffset 값은 변수에 담도록 하겠다.
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
scrollLoop();
})
setLayout();
})()
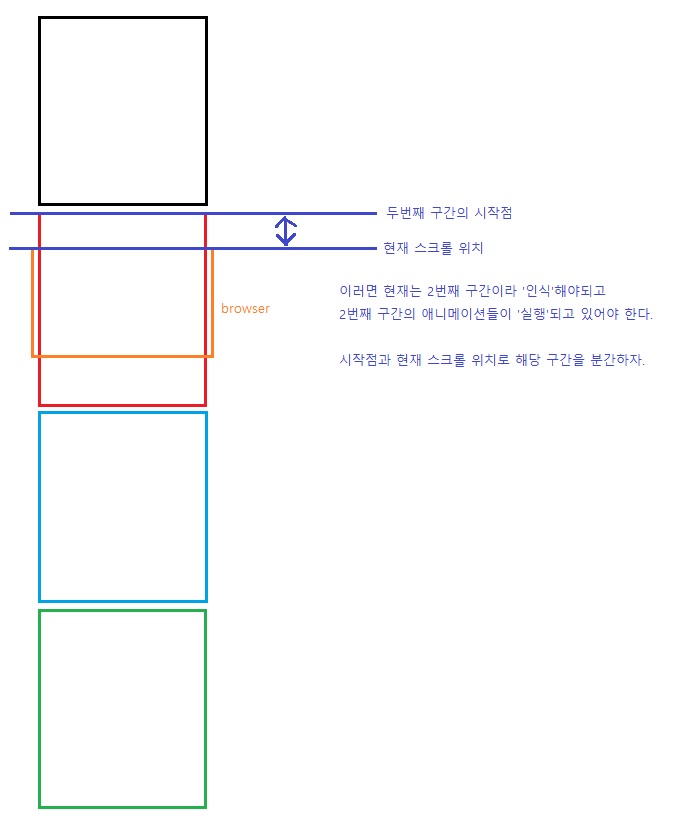
11. 현재 활성시킬 씬 결정하기
- 계산은 치밀하게 해야된다.
iOS 스크롤 바운스 - 마이너스 영역일 때를 주의해야된다.
매번 브라우저 업데이트 때마다 스펙은 달라지지만iOS safari브라우저에선 바운스현상일 때도scroll이벤트가 발생하는 것으로 기억한다.
다른 브라우저는 바운스 현상 때scroll이벤트가 발생안했던 걸로 기억한다.
여튼 바운스 현상 때scroll이벤트가 발생한다면 아래 코드에서 오류가 생길 수도 있다.currentScene변수값이 - 값이 될 수도 있다.
이런 거에서 에러가 발생할 수 있다.
이런 경우를 방지해야된다.아래와 같이 안전장치를 넣어주자.
(() => {
let yOffset = 0; // window.pageYOffset 대신 쓸 변수
let prevScrollHeight = 0; // 현재 스크롤 위치(yOffset)보다 이전에 위치한 스크롤 섹션들의 스크롤 높이값의 합
let currentScene = 0; // 현재 활성화된(눈 앞에 보고있는) 씬(scroll-section)
const sceneInfo = [
{
// 0
type: 'sticky',
heightNum : 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0'),
}
},
{
// 1
type: 'normal',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-1'),
}
},
{
// 2
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-2'),
}
},
{
// 3
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-3'),
}
}
];
function setLayout() {
// 각 스크롤 섹션의 높이 세팅
for (let i = 0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight = sceneInfo[i].heightNum * window.innerHeight;
sceneInfo[i].objs.container.style.height = `${sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight}px`;
}
}
function scrollLoop() {
prevScrollHeight = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < currentScene; i++ ) {
prevScrollHeight += sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight;
}
if (yOffset > prevScrollHeight + sceneInfo[currentScene].scrollHeight) {
currentScene++;
}
if (yOffset < prevScrollHeight) {
if (currentScene === 0) return; // 브라우저 바운스 효과로 인해 마이너스가 되는 것을 방지(모바일) - 내가볼땐 iOS를 대비하기 위함인거같음
currentScene--;
}
}
// resize도 고려
window.addEventListener('resize', setLayout);
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
scrollLoop();
})
setLayout();
})()
12. 현재 활성 씬 반영하기
(() => {
let yOffset = 0; // window.pageYOffset 대신 쓸 변수
let prevScrollHeight = 0; // 현재 스크롤 위치(yOffset)보다 이전에 위치한 스크롤 섹션들의 스크롤 높이값의 합
let currentScene = 0; // 현재 활성화된(눈 앞에 보고있는) 씬(scroll-section)
const sceneInfo = [
{
// 0
type: 'sticky',
heightNum : 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0'),
}
},
{
// 1
type: 'normal',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-1'),
}
},
{
// 2
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-2'),
}
},
{
// 3
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-3'),
}
}
];
function setLayout() {
// 각 스크롤 섹션의 높이 세팅
for (let i = 0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight = sceneInfo[i].heightNum * window.innerHeight;
sceneInfo[i].objs.container.style.height = `${sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight}px`;
}
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
let totalScrollHeight = 0;
for (let i=0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
totalScrollHeight += sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight;
if (totalScrollHeight >= yOffset) {
currentScene = i;
break;
}
}
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
function scrollLoop() {
prevScrollHeight = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < currentScene; i++ ) {
prevScrollHeight += sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight;
}
if (yOffset > prevScrollHeight + sceneInfo[currentScene].scrollHeight) {
currentScene++;
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
if (yOffset < prevScrollHeight) {
if (currentScene === 0) return; // 브라우저 바운스 효과로 인해 마이너스가 되는 것을 방지(모바일) - 내가볼땐 iOS를 대비하기 위함인거같음
currentScene--;
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
}
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
scrollLoop();
});
// DOMContentLoaded / load 메서드 차이점 : load는 페이지의 이미지 같은 리소스들이 전부 로드되어야 발생하는 이벤트이다.
// DOMContentLoaded는 DOM html 객체들 로드만 끝나면 바로 실행을 한다.
// DOMContentLoaded 가 실행시점이 load 보다 빠르다.
// window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', setLayout);
window.addEventListener('load', setLayout); // 초기화 함수, 다 load 된 이후에 실행되도록
window.addEventListener('resize', setLayout);
})()
13. 스트롤 애니메이션 구현 1
(() => {
let yOffset = 0; // window.pageYOffset 대신 쓸 변수
let prevScrollHeight = 0; // 현재 스크롤 위치(yOffset)보다 이전에 위치한 스크롤 섹션들의 스크롤 높이값의 합
let currentScene = 0; // 현재 활성화된(눈 앞에 보고있는) 씬(scroll-section)
const sceneInfo = [
{
// 0
type: 'sticky',
heightNum : 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0'),
messageA: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.a'),
messageB: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.b'),
messageC: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.c'),
messageD: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.d'),
},
values: {
messageA_opacity: [0, 1]
}
},
{
// 1
type: 'normal',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-1'),
}
},
{
// 2
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-2'),
}
},
{
// 3
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-3'),
}
}
];
function setLayout() {
// 각 스크롤 섹션의 높이 세팅
for (let i = 0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight = sceneInfo[i].heightNum * window.innerHeight;
sceneInfo[i].objs.container.style.height = `${sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight}px`;
}
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
let totalScrollHeight = 0;
for (let i=0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
totalScrollHeight += sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight;
if (totalScrollHeight >= yOffset) {
currentScene = i;
break;
}
}
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
function playAnimation() {
switch (currentScene) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
break;
case 2:
break;
case 3:
break;
default:
break;
}
}
function scrollLoop() {
prevScrollHeight = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < currentScene; i++ ) {
prevScrollHeight += sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight;
}
if (yOffset > prevScrollHeight + sceneInfo[currentScene].scrollHeight) {
currentScene++;
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
if (yOffset < prevScrollHeight) {
if (currentScene === 0) return; // 브라우저 바운스 효과로 인해 마이너스가 되는 것을 방지(모바일) - 내가볼땐 iOS를 대비하기 위함인거같음
currentScene--;
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
playAnimation();
}
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
scrollLoop();
});
window.addEventListener('load', setLayout); // 초기화 함수, 다 load 된 이후에 실행되도록
window.addEventListener('resize', setLayout);
})()
14. 스크롤 애니메이션 구현 2 ~ 4
- 각 섹션마다의 상대적 스크롤 위치
- 첫번째 섹션의 text 애니메이션 - 첫번째 섹션 안에 있지만 그 안에서도 등장하는 위치와 사라지는 위치가 다 다르다.
즉,keyframe개념이 필요하다.
keyframe이란?
애니메이션 진행 중 중간중간 변화가 일어나는 지점을 keyframe 이라고 한다.
이를 계산해서 처리하는 코드도 넣어줘야된다.
scene이 바뀌는 찰나, 그 순간에 값이 이상하게 계산되는 경우가 있다.
enterNewScene변수를 활용하여true/false값으로 이를 방지하자.
(() => {
let yOffset = 0; // window.pageYOffset 대신 쓸 변수
let prevScrollHeight = 0; // 현재 스크롤 위치(yOffset)보다 이전에 위치한 스크롤 섹션들의 스크롤 높이값의 합
let currentScene = 0; // 현재 활성화된(눈 앞에 보고있는) 씬(scroll-section)
let enterNewScene = false; // 새로운 scene이 시작된 순간 true
const sceneInfo = [
{
// 0
type: 'sticky',
heightNum : 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0'),
messageA: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.a'),
messageB: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.b'),
messageC: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.c'),
messageD: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-0 .main-message.d'),
},
values: {
messageA_opacity: [0, 1]
}
},
{
// 1
type: 'normal',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-1'),
}
},
{
// 2
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-2'),
}
},
{
// 3
type: 'sticky',
heightNum: 5,
scrollHeight: 0,
objs: {
container: document.querySelector('#scroll-section-3'),
}
}
];
function setLayout() {
// 각 스크롤 섹션의 높이 세팅
for (let i = 0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight = sceneInfo[i].heightNum * window.innerHeight;
sceneInfo[i].objs.container.style.height = `${sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight}px`;
}
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
let totalScrollHeight = 0;
for (let i=0; i < sceneInfo.length; i++) {
totalScrollHeight += sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight;
if (totalScrollHeight >= yOffset) {
currentScene = i;
break;
}
}
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
function calcValues(values, currentYOffset) {
let rv;
// 현재 씬(스크롤섹션)에서 스크롤된 범위를 비율로 구하기
let scrollRatio = currentYOffset / sceneInfo[currentScene].scrollHeight;
rv = scrollRatio * (values[1] - values[0]) + values[0];
return rv;
}
function playAnimation() {
const objs = sceneInfo[currentScene].objs;
const values = sceneInfo[currentScene].values;
const currentYOffset = yOffset - prevScrollHeight;
switch (currentScene) {
case 0:
let messageA_opacity_in = calcValues(values.messageA_opacity, currentYOffset);
objs.messageA.style.opacity = messageA_opacity_in;
break;
case 1:
break;
case 2:
break;
case 3:
break;
default:
break;
}
}
function scrollLoop() {
enterNewScene = false;
prevScrollHeight = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < currentScene; i++ ) {
prevScrollHeight += sceneInfo[i].scrollHeight;
}
if (yOffset > prevScrollHeight + sceneInfo[currentScene].scrollHeight) {
enterNewScene = true;
currentScene++;
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
if (yOffset < prevScrollHeight) {
enterNewScene = true;
if (currentScene === 0) return; // 브라우저 바운스 효과로 인해 마이너스가 되는 것을 방지(모바일) - 내가볼땐 iOS를 대비하기 위함인거같음
currentScene--;
ducument.body.setAttribute('id', `show-scene-${currentScene}`);
}
// scene이 바뀌는 찰나 값 이상하게 적용되는 오류 건너뛰기 위함
// scene이 바뀌는 순간 음수값이나 이상한 값들이 찍힐 때가 있음
if (enterNewScene) return;
playAnimation();
}
window.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
yOffset = window.pageYOffset;
scrollLoop();
});
window.addEventListener('load', setLayout); // 초기화 함수, 다 load 된 이후에 실행되도록
window.addEventListener('resize', setLayout);
})()