전문가처럼 코딩하는 9가지 자바스크립트 트릭!
최신 기술, 팁 및 트릭을 사용하여 전문 JavaScript 개발자처럼 코딩
자바스크립트를 처음 사용했을 무렵 난 코드를 아주 레거시하게 작성했었다.
때문에 모던 자바스크립트를 활용하여 코드를 다시 수정해야만했고 간결하고 단순하게 만들기 위해 여러번 수정을 거쳐야했다.
오늘은 코드 품질을 개선하고 다음 앱을 코딩할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있도록 특별한 순서없이 자바스크립트의 상위 9가지 팁, 트릭 및 기능을 공유하도록 하겠다.
1. Arrow Function
ES6는 Arrow Functions을 도입하여 함수 코드를 훨씬 더 깔끔하고 전체적으로 빠르게 작성할 수 있도록 했다.
const multiply = function(x, y) {
return x * y;
};
위와 같이 함수를 선언하는 대신
const multiply = (x, y) => {
return x * y;
};
위와 같은 식으로 선언할 수 있게 되었다.
표현식(리턴되는 식)이 하나만 있는 경우는 아래처럼 더 단순화해서 쓸 수 있다.
const multiply = (x, y) => x * y;
2. Spread Operator …
스프레드 연산자를 사용하면 0개 이상의 인수(함수 호출용) 또는 요소(배열 리터럴용)가 예상되는 위치에서 배열 표현식 또는 문자열과 같은 반복 가능 항목을 확장하거나 0또는 0인 위치에서 객체 표현식을 확장할 수 있다.
더 많은 키-값 쌍(객체리터럴용)이 필요하다.
기존 배열을 일부로 사용하여 새 배열 만들기
const parts = ['shoulders', 'knees'];
const lyrics = ['head', ...parts, 'and', 'toes'];
console.log(lyrics);
// Result: ["head", "shoulders", "knees", "and", "toes"]
배열을 연결하는 더 좋은 방법
let arr1 = [0, 1, 2];
let arr2 = [3, 4, 5];
arr1 = [...arr1, ...arr2];
console.log(arr1) // Result: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
배열의 요소를 함수에 대한 인수로 사용
const add = (a, b, c) => a + b + c;
let array = [1,2,3];
console.log(add(...array)); // Result: 6
3. Rest Operator
Rest 구문은 스프레드 구문과 똑같이 보이지만 배열과 객체를 분해하는 데 사용됩니다.
어떤면에서 나머지 구문은 스프레드 구문과 반대입니다.
스프레드 구문은 배열을 요소로 확장하고 나머지 구문은 여러 요소를 수집하여 단일 요소로 압축합니다.
const blend = (ice, liquid, ...theRest) => {
console.log(theRest);
};
blend('ice', 'milk', 'banana', 'strawberry');
// Result: ['banana', 'strawberry']
함수의 마지막 매개 변수 앞에 …를 붙일 수 있습니다.
그러면 나머지 모든 인수가 자바스크립트 배열 내에 배치됩니다.
4. Fill Arrays
한 줄로 간단한 배열 만들기
An array of 5 empty strings
let array = Array(5).fill(''); // Result: ['', '', '', '', '']
An Array of numbers from 0 to 4
let array = Array.from(Array(5).keys()); // Result: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
// Using the spread operator
let array = [...Array(5).keys()] // Result: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
5. Computed object property names
ES6는 계산 된 객체 속성 이름을 지원하므로 표현식을 대괄호 [] 안에 넣을 수 있으며, 이는 속성 이름 / 키로 계산되고 사용됩니다.
let key = 'A_DYNAMIC_KEY';
let obj = {
[key]: 'A_VALUE',
};
console.log(obj) // Result: { A_DYNAMIC_KEY: 'A_VALUE' }
6. Good ways to console.log()
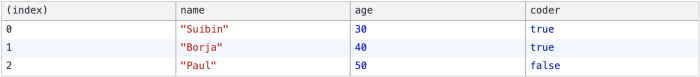
객체 배열이있는 경우 console.table()을 사용하십시오.
const foo = { name: 'Suibin', age: 30, coder: true };
const bar = { name: 'Borja', age: 40, coder: true };
const baz = { name: 'Paul', age: 50, coder: false };
console.table([foo, bar, baz]);
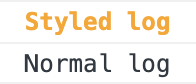
’%’기호를 사용하여 맞춤 CSS 스타일링으로 데이터를 돋보이게합니다.
console.log('%cStyled log', 'color: orange; font-weight: bold;');
console.log('Normal log');
하나의 콘솔 로그에 여러 개체를 기록하여 코드 공간을 줄이고 어떤 변수가 데이터를 정의하는지 확인
const foo = { name: 'Suibin', age: 30, coder: true };
const bar = { name: 'Borja', age: 40, coder: true };
const baz = { name: 'Paul', age: 50, coder: false };
console.log({ foo, bar, baz });

7. Object destructuring
필요한 객체 속성을 해체하여 코드 반복을 제거합니다.
const dog = {
name: 'Nala',
gender: 'female',
age: 10
};
const func = ({ name, age }) => {
return `${name} is ${age} years old.`;
};
console.log(func(dog)); // Result: Nala is 10 years old.
사용하려는 속성의 이름을 괄호로 묶어 함수 인수 내부의 구조를 분해합니다.
또는
동물 개체를 전달하고 개체의 속성 이름이 개체와 동일한 변수를 설정합니다.
단일 함수에서 구조를 분해 할 여러 개체가있는 경우 더 좋습니다.
const dog = {
name: 'Nala',
gender: 'female',
age: 10
};
const func = (animal) => {
const { name, age } = animal;
return `${name} is ${age} years old.`;
};
console.log(func(dog)); // Result: Nala is 10 years old.
8. Use reduce() map() and filter() instead of regular for loops
reduce() 메서드를 사용하여 배열을 단일 값으로 줄입니다.
let orders = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const total = orders.reduce((acc, cur) => acc + cur);
console.log(total); // Result: 15
map() 메서드를 사용하여 모든 배열 요소에 대해 함수를 호출 한 결과로 새 배열을 만듭니다.
let orders = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const total = orders.map((item) => item * 2);
console.log(total); // Result: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
filter() 메서드를 사용하여 테스트를 통과 한 모든 배열 요소로 채워진 배열을 만듭니다 (함수로 제공됨).
let orders = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const total = orders.filter((item) => item > 3);
console.log(total); // Result: [4, 5]
9. Conditional Operator (조건부 연산자)
다음 구문을 사용하여 모든 if..else 문을 조건문으로 변경할 수 있습니다.
condition ? (expression if true) : (expression if false)
예를 들면, 다음과 같은 코드이다.
const hour = 5;
if (hour < 18) {
console.log('Good day');
} else {
console.log('Good evening');
}
// Result: Good day
다음과 같이 줄일 수 있습니다.
const hour = 5;
hour < 18 ? console.log('Good day') : console.log('Good evening');
// Result: Good day